AI Application Development Guide

Insights
Table Of Content
What Is AI Application Development?
When Does AI Application Development Make Sense?
Types of AI Applications Businesses Actually Build
Key Components of an AI Application
AI Application Development vs Traditional App Development
The Advantages of Building an AI App
Common Challenges and Risks in AI Application Development
AI Application Development Cost in 2026
Industries Using AI Applications Today
AI Application Trends That Actually Matter in 2026
Is It Worth Building Generative AI Applications in 2026 and Beyond?
How to Approach AI Application Development Successfully
Final Thoughts
Frequently Asked Questions
AI Application Development Services: Building Intelligent Apps That Solve Real Problems
Expert guide to AI application development services in 2026. Learn what AI apps cost, how long they take to build, and why data readiness matters more than algorithms
17 Sep 2025
AI is no longer optional for any businesses these days.
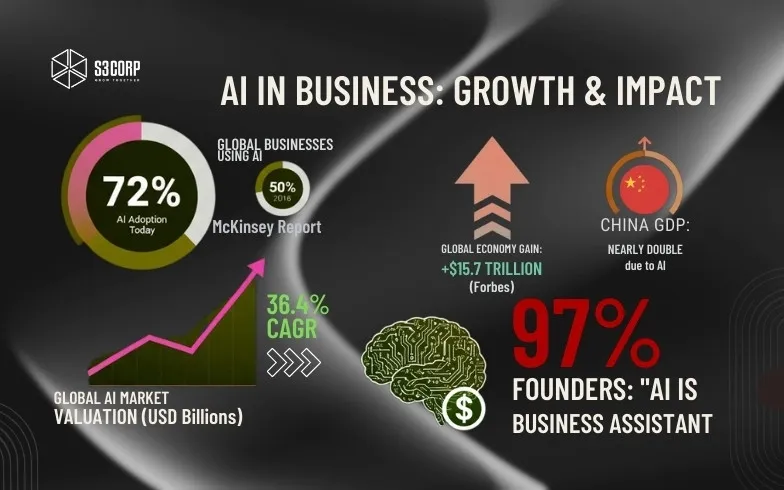
Today, 72 percent of companies report using AI in some form, while six years ago, adoption rates held at just 50 percent, according to McKinsey. The global market was valued at $92.8 billion in 2021 and is forecast to reach $1129 billion by 2030, growing at a rate of 36.4 percent annually. Forbes also projects that AI will contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with China nearly doubling its GDP as a result of AI integration, while a projected 97% of founders expected AI to help their business.
With this in mind: AI is no longer a futuristic concept. It is progressively changing the way businesses operate today.
AI is used in customer service as a virtual assistant, improves banking through detecting fraud, and is used in manufacturing for predictive analytics. AI is also now transforming the way personalization and efficiency works in the Health and Educational systems. There is also a rise in expectation, as well as, competition in the AI market with the introduction of generative AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and Llama.
In spite of the momentum, developing AI applications is still challenging. It is instructive to relate real-world challenges to the appropriate technology to use. Challenges include the intricacies of data, the desire to merge data with older platforms, potential security threats, and finding the right AI use cases. In many cases, leaders tend to take longer than planned to move from pilot projects to production and find it hard to optimize the use of AI throughout the organization.
As for AI, it is supposed to help with cost reduction, faster scaling, improved decision-making, and workflow automation. As much as these benefits are appealing and real, the journey to achieve them is not easy. Initially, they face the question of, Which AI applications will be deployable and useful? How will the new applications relate to the existing systems? What value will they actually add?
This article is the start of you being able to strategically move forward. You will understand the core of developing AI applications which entails defining the relevant business challenges and building and deploying appropriate robust solutions.
What Is AI Application Development?
AI application development means building software that makes decisions or predictions without explicit programming for every scenario. Instead of writing "if-then" rules, developers train models on data. These models learn patterns and apply them to new situations.
Traditional software follows exact instructions. AI software adapts based on what it learned during training. A traditional search function matches keywords. An AI-powered search understands intent, context, and even corrects mistakes.
Companies invest in AI application development because certain problems can't be solved with traditional code. When you need to process unstructured data at scale, predict future outcomes, or personalize experiences for millions of users, AI becomes the practical choice.
The technology reached an inflection point in 2023 with generative AI. Now businesses can build applications that write, analyze images, summarize documents, and hold conversations. Custom AI application development services help companies integrate these capabilities into their actual workflows, not just experiment with demos.
When Does AI Application Development Make Sense?
Not every problem needs AI. Some organizations waste months building AI solutions for problems that traditional software handles better, faster, and cheaper.
AI works well when you need to:
Process large volumes of unstructured data like documents, images, audio, or video. Traditional software struggles here. AI thrives.
Make predictions based on historical patterns. Credit risk, equipment failure, customer churn—these benefit from machine learning models that spot subtle indicators humans miss.
Personalize experiences at scale. Recommendation engines, dynamic pricing, and content matching require analyzing millions of data points per user.
Automate repetitive cognitive tasks. Document classification, invoice processing, customer service routing—tasks humans can do but shouldn't have to.
AI should NOT be used when:
Your rules are simple and stable. If you can write clear logic that rarely changes, traditional code works better and costs less.
You lack quality data. AI models need examples to learn from. No data means no AI, regardless of how sophisticated your algorithms are.
Explainability is legally required. Some AI models function as black boxes. If you must explain every decision in court, think twice.
The problem has zero tolerance for errors. AI systems make mistakes. A 95% accuracy rate means 5% failures. Can your business accept that?
Common false assumptions include:
"AI will figure out what we need." No. AI needs clearly defined problems and success metrics. Vague goals produce vague results.
"More data always helps." Wrong. Bad data in larger quantities produces worse results. Quality beats quantity every time.
"AI replaces our team." Rarely. AI typically augments human work rather than replacing it completely.
Types of AI Applications Businesses Actually Build
The media loves showcasing futuristic AI demos. Real businesses build more practical applications that directly impact revenue or reduce costs.
Generative AI applications create new content based on patterns learned from training data. Companies build internal tools that draft customer responses, generate product descriptions, summarize meeting transcripts, or create marketing variations. These applications don't replace creative teams—they handle the repetitive parts so humans focus on strategy.
Predictive analytics systems forecast future outcomes using historical data. Retailers predict inventory needs. Manufacturers predict equipment failures before they happen. Banks predict which customers will default. These systems turn data into foresight, helping teams make better decisions faster.
Recommendation engines suggest products, content, or actions based on user behavior. E-commerce sites show relevant products. Streaming platforms suggest shows. B2B platforms recommend next actions for sales teams. Good recommendation engines feel helpful, not pushy.
Conversational AI handles communication through chatbots, voice assistants, or automated support systems. Modern conversational AI understands context, handles complex requests, and escalates appropriately to humans. These applications reduce support costs while improving response times.
Computer vision applications extract meaning from images and video. Quality control systems inspect products on assembly lines. Security systems identify unusual behavior. Healthcare applications analyze medical images. Logistics companies track packages and shipments automatically.
Each application type solves specific business problems. Enterprise AI development services help organizations identify which type fits their needs, then build it properly.
Key Components of an AI Application
AI applications share common building blocks. Understanding these components helps you evaluate vendors, estimate costs, and spot potential problems early.
Data forms the foundation. AI models learn from examples, so you need relevant, clean, labeled data. For a fraud detection system, you need historical transaction data marked as fraudulent or legitimate. For a document classifier, you need documents tagged by category. Data collection, cleaning, and labeling often consume more time and budget than model development.
Models are the decision-making engines. These mathematical structures learn patterns from your data. Some models predict numbers (sales forecasts). Others classify items into categories (spam or not spam). Still others generate new content (product descriptions). Models require training, validation, and continuous monitoring to maintain accuracy.
Infrastructure runs everything. AI applications need computing power for training models and serving predictions. Cloud platforms offer AI-optimized hardware that scales based on demand. On-premise solutions give more control but require significant upfront investment. Edge deployment runs models locally on devices for faster response times and better privacy.
Integration connects AI to existing systems. Your AI model needs to receive data from your CRM, ERP, or data warehouse. Its predictions need to flow back into business applications where teams actually work. APIs, data pipelines, and middleware handle these connections. Poor integration ruins otherwise excellent AI models.
Monitoring and governance ensure reliability. AI models drift over time as real-world patterns change. Monitoring tracks prediction accuracy, response times, and resource usage. Governance includes access controls, audit trails, and compliance tracking. These unglamorous components separate production-ready AI from science experiments.
AI Application Development vs Traditional App Development
The development process differs significantly between AI and traditional applications. These differences affect timelines, costs, and risks.
Decision-making changes fundamentally. Traditional apps execute predetermined logic. AI apps make probabilistic decisions based on learned patterns. This means you define business rules for traditional apps but provide training examples for AI apps. Testing also differs—AI requires validating model behavior across diverse scenarios, not just checking that functions execute correctly.
Costs follow different patterns. Traditional apps have predictable development costs based on features and complexity. AI application development costs include data preparation, experimentation, and ongoing model improvement. Initial AI projects often exceed budget because teams underestimate data work. However, AI apps scale better—adding new use cases reuses existing infrastructure.
Maintenance never ends. Traditional apps need updates for bugs and new features. AI applications require continuous retraining as data patterns shift. A fraud detection model trained in 2023 performs worse in 2025 because fraud tactics evolve. Budget for ongoing AI model improvement, not just initial development.
Risk profiles differ dramatically. Traditional apps fail predictably when code has bugs. AI apps fail unpredictably when models encounter unusual inputs. A chatbot might work perfectly in testing but give bizarre responses to unexpected questions. Secure AI development practices include extensive testing, guardrails, and fallback mechanisms.
Traditional Apps vs AI Apps Comparison
|
Feature |
Traditional Apps |
AI Apps |
|
Updates |
Manual upgrades required |
Learns and updates itself with data |
|
Task Execution |
Runs only with user input |
Automates workflows and offers predictions |
|
User Experience |
Limited personalization |
Context-aware and dynamic |
|
Data Handling |
Works with structured, predefined data |
Analyzes large, unstructured, real-time data |
|
Learning |
Fixed after release |
Improves through machine learning cycles |
|
Logic |
Predefined instructions only |
Adaptive algorithms that refine outcomes |
|
Interaction |
Static responses |
Evolves based on user behavior |
|
Media Processing |
Basic handling of text, files |
Processes images, video, and audio efficiently |
|
Performance |
Reliable for repeatable tasks |
Optimized for complex and data-heavy tasks |
|
Examples |
ERP tools, CRM, spreadsheets |
Virtual assistants, recommendation systems, smart devices |
The Advantages of Building an AI App
Personalized Experiences
AI apps study user activity with the aim of providing customized experiences. By analyzing previous interactions, your app can suggest and recommend products, services, and content that makes it more useful and interactive. Leaders in ecommerce and streaming services use AI in this manner to maximize user satisfaction and retention.
Smarter Decisions
Shifting the customer experience paradigm, AI analyzes data in real time, providing decision-making insights. Customer face time, market fluctuations, and operational lags all rely on the accuracy of AI, and even more so on precision AI. Instinct no longer acknowledges the presence of a competitive edge and, therefore, is of no value in decision-making. Based on the leadership team's conclusions, intelligent predictions just trump instinct.
Supervised Automation
AI takes over monotonous. From scheduling and customer query tickets to inventory management, AI systems can automate a wide range of tasks without the need for manual supervision. These automated systems are incredibly valuable, as they reduce manual errors, lower operational costs, and free up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. Most importantly, these responsive systems are vital for a company's growth as the workload increases.
Proactive and Interactive Engagement
AI systems are more proactive. They can remind the user of tasks, workouts, and deadlines. AI-powered chatbots are developed to replace waiting. Users can anticipate the response in real time and after a few minutes. With advanced emotional recognition, these systems encourage users more of a delightful interface alongside feeling more human.
Voice Search and Conversational Interfaces
Like voice-enabled technological and conversational UIs, voice search allows users to access any type of information quickly, and voice conversing UIs simplifies and intuitive information interface. Rather than using menus and forms, users can communicate or speak with an app in friendly conversations. This enhancement in user interface allows seamless interaction in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, e-commerce, and customer service, broadening the scope of user interaction.
Real-time Translation and Content Insights
AI tools with real-time translations break down the language barrier and make apps accessible to a global audience. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) spans text on images and PDFs and converts it to other usable formats, expanding content accessibility. Content data insights enable your app to respond and tailor information to user specifications in a given region and domain. This increases the regional and cross domain impact of the app.
Scalability and Performance
Increased need and access to AI tools can be observed all over the world. With the growing number and volume of users, these AI tools can also be scaled up without the need for redesigning, ensuring performance and reliability without compromising on quality or speed.
Security and Risk Management
AI augments security with real-time anomaly detection and predictive analytics. Algorithms can uncover and address potential threats that conventional methods lack. This will ensure a higher degree of security on private data and instill confidence among users. For firms operating on sensitive data, advanced security is not only a necessity but also a competitive advantage.
Competitive Edge
Creating an AI application helps in AI Business differentiation from competitors in an overcrowded market. Enhanced customer experience, streamlined operations, and better decision making are some things that will tell your business apart from the rest. For startups and enterprises, making an early investment in AI will position your business as an industry leader and help in sustaining business growth.
Common Challenges and Risks in AI Application Development
Every AI project faces predictable obstacles. Knowing them in advance helps you plan effectively and avoid catastrophic failures.
Data quality problems derail more projects than any other factor. Missing values, inconsistent formats, incorrect labels, outdated information—these data issues compound during model training. A model trained on bad data produces bad predictions regardless of algorithmic sophistication. Budget significant time for data cleaning and validation. Expect to spend 50-70% of your AI project timeline on data work.
Cost overruns surprise even experienced teams. AI application development cost estimates often miss crucial expenses: data labeling services, specialized hardware for training, API costs for pre-trained models, extended testing periods, and ongoing monitoring infrastructure. Initial estimates rarely include the full end-to-end AI development cycle. Add 30-40% contingency to quoted prices for realistic budgeting.
Talent shortages affect both hiring and partnerships. Experienced AI engineers remain scarce and expensive. An AI software development company with proven delivery history charges premium rates because their expertise is genuinely rare. If costs seem surprisingly low, question whether the provider has real AI experience or just traditional development skills with AI buzzwords.
Bias and compliance create legal exposure. AI models learn from historical data, which often contains human biases. A hiring tool trained on past decisions might discriminate. A credit model might unfairly disadvantage certain demographics. Regulations like GDPR in Europe and emerging AI laws globally impose strict requirements on AI systems. Compliance isn't optional—it's foundational.
Scaling from prototype to production reveals hidden complexity. An AI model that works perfectly on 1,000 test cases might behave strangely on 1,000,000 production cases. Latency becomes a problem. Edge cases multiply. Infrastructure costs explode. Scalable AI architecture requires planning from day one, not retrofitting after launch.
Read More: Artificial Intelligence Challenges Enterprises Face in 2026
AI Application Development Cost in 2026
The most common question about AI projects: "What will this cost?" The honest answer: "It depends on about 20 variables." But some realistic ranges help with planning.
MVP versus full product costs differ by magnitude. A minimum viable AI product solving one specific problem costs $50,000-$150,000 for most business applications. This includes data preparation, model development, basic integration, and initial deployment. A full-featured enterprise AI solution with multiple use cases, comprehensive integration, and production-grade infrastructure runs $300,000-$1,000,000+.
Major cost drivers include:
Data work consumes 40-50% of budgets. Collecting, cleaning, labeling, and organizing data requires significant human effort, especially for supervised learning where humans must label training examples.
Model complexity affects costs exponentially. Simple classification models cost less than complex generative AI systems. Custom models cost more than fine-tuned pre-trained models. Specialized models for niche applications cost the most.
Integration depth determines software development effort. Connecting to a single API differs vastly from integrating with multiple legacy systems. Real-time data pipelines cost more than batch processing. Bidirectional integration costs more than one-way.
Infrastructure requirements scale with usage. Cloud AI services charge per prediction, per training hour, or per data processed. A prototype serving 100 requests daily costs little. A production system serving 100,000 requests daily costs significantly more.
Compliance and security add 20-30% for regulated industries. Healthcare, finance, and government face stricter requirements. Audit trails, explainability tools, and extensive testing increase costs but aren't optional.
Realistic ranges by application type:
Chatbot with existing large language model integration: $40,000-$100,000
Predictive analytics dashboard: $60,000-$150,000
Custom computer vision application: $80,000-$200,000
Recommendation engine: $70,000-$180,000
Enterprise generative AI platform: $250,000-$800,000
Why AI ROI comes later than expected: Traditional software creates value immediately after deployment. AI applications need time to prove value. Models require refinement based on real-world feedback. Users need training on new AI-augmented workflows. Organizational processes must adapt. Plan for 6-12 months before seeing full return on investment, even with successful implementations.
Industries Using AI Applications Today
AI applications have moved beyond tech companies into practically every industry. Real businesses solve real problems with AI, generating measurable returns.
Healthcare organizations use AI for diagnosis support, medical imaging analysis, and patient monitoring. Radiology departments deploy computer vision to detect anomalies in X-rays and MRIs faster than human review alone. Hospitals use predictive models to forecast patient deterioration, enabling preventive intervention. Pharmaceutical companies accelerate drug discovery using AI to simulate molecular interactions. These applications directly impact patient outcomes while reducing costs.
Finance companies build AI for fraud detection, risk assessment, and trading. Credit card processors analyze millions of transactions in real-time, flagging suspicious patterns. Banks use AI models to evaluate loan applications, processing decisions in minutes instead of days. Investment firms deploy machine learning for algorithmic trading and portfolio optimization. Compliance teams use AI to monitor communications and detect regulatory violations.
E-commerce platforms depend on AI for recommendations, pricing, and search. Product recommendation engines drive significant percentage of revenue for major retailers. Dynamic pricing algorithms adjust costs based on demand, competition, and inventory levels. Visual search lets customers find products by uploading photos. Virtual try-on applications use computer vision to show how products look on individual customers.
Manufacturing operations deploy AI for quality control, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization. Factory floor cameras inspect products for defects faster and more consistently than human inspectors. Sensors monitor equipment health, predicting failures before they cause downtime. AI models optimize production schedules, balancing efficiency with quality requirements. Supply chain systems forecast demand and optimize inventory across distribution networks.
Logistics companies use AI for route optimization, demand forecasting, and warehouse automation. Delivery route planning considers traffic patterns, weather, and package priorities in real-time. Demand forecasting helps warehouses stock the right products in the right locations. Computer vision guides robots in picking and packing operations. These applications reduce costs while improving delivery speed.
Education platforms implement AI for personalized learning, automated grading, and student support. Adaptive learning systems adjust content difficulty based on individual student performance. Automated essay grading provides instant feedback on written assignments. Chatbots answer common student questions 24/7, reducing support burden on faculty. Early warning systems identify struggling students before they fail courses.
AI Application Trends That Actually Matter in 2026
Industry trends come and go, but several developments genuinely impact how businesses build AI applications today.
Generative AI integration transforms knowledge work. Large language models now power applications for content creation, code generation, data analysis, and decision support. Businesses build custom AI applications that combine retrieval-augmented generation with their proprietary data, creating AI assistants that know company-specific information. This trend accelerates productivity for roles involving writing, research, and analysis.
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) solves the knowledge problem. Pure generative AI models hallucinate—they confidently state incorrect information. RAG systems retrieve relevant documents before generating responses, grounding answers in verified sources. This architectural pattern makes generative AI development services practical for business applications where accuracy matters. Expect most enterprise AI applications to adopt RAG patterns.
Edge AI brings processing to devices. Instead of sending data to cloud servers, edge AI runs models directly on smartphones, cameras, sensors, and other devices. This reduces latency, improves privacy, and works without internet connectivity. Manufacturing, healthcare, and retail increasingly deploy edge AI for real-time processing where milliseconds matter or data sensitivity prohibits cloud transmission.
Responsible AI moves from philosophy to practice. Regulations force companies to document AI decision-making processes. Customers demand transparency about AI usage. Responsible AI frameworks help development teams build fairness testing, bias detection, and explainability into applications from the start. This isn't just compliance theater—poorly designed AI systems create genuine business and legal risks.
AI security becomes a distinct discipline. Traditional cybersecurity doesn't fully protect AI systems. Adversarial attacks manipulate model inputs to cause incorrect predictions. Data poisoning corrupts training data to compromise model behavior. Model theft extracts proprietary AI capabilities. Security practices for AI application development now include adversarial testing, input validation, and model monitoring for unusual behavior.
Is It Worth Building Generative AI Applications in 2026 and Beyond?
Market Growth Signals Strong Potential
Generative AI is not letting up anytime soon. As per studies, the market is likely to grow from 36 billion USD in 2024 to 415 billion USD in 2027. In 2030, the forecast is approximately 184 billion USD. This level of growth is among the most rapidly developing in the technology vertical. Companies in finance, healthcare, retail, entertainment, and manufacturing are infusing AI within their foundational processes. The need is not confined to large technology behemoths. All businesses, regardless of their stature, are pursuing tools that augment productivity and curtail overhead expenses. If you planning to develop an AI application, these quoted figures give you an opportunity worth exploring.
Funding Trends Show Mixed Signals
Since 2021, financing for startups has decreased, plummeting by over 60% on a global monthly average. This indicates that acquiring capital has become more challenging. However, within the sector of AI, there appears to be a bias. Investors continue to put billions into firms at the frontiers of AI research and infrastructure. OpenAI, for instance, just raised 6.6 billion USD, and xAI, founded by Elon Musk, also recently closed several substantial rounds. Most of the funding is dispersed among firms developing core models and foundational technology for AI. Startups focused on applying these models in specific niches face more competition for capital and need stronger value propositions to attract investors.
Opportunities for Startups Still Exist
For as long as there are startups that are positioned well, there will always be possibilities for them regardless of the filtered economic circumstances. The area of Gen- AI is still believed to be promising, however, the outcome is always dependent on the way the idea is carried out. The failure rate for startups is particularly grim, and AI projects are certainly no outliers. A reliable method to go down is building a Gen AI applications where there is no problem to solve. Failing to deliver measurable and tangible business value is always the issue. The value has to deliver business value, and here, the values of AI are clear, offering Automation of repetitive tasks, Assisting in enhances personalization, and Assisting in rapid Decision making. There is always a sure chance to succeed for the businesses that fill the gaps in current problems and offer dependable and scalable tools.
Key Questions for Decision-Makers
Before committing resources to generative AI development, evaluate your strategic position. Does your team have the technical expertise to deliver a high-performing solution? Can your application scale to handle growing data and user demands? Is your use case distinct enough to compete against both large incumbents and agile startups? Building an AI product in 2026 is not about chasing trends. It is about solving real problems with sustainable technology. If you have a strong business case and a clear plan for differentiation, the market conditions support long-term growth.
How to Approach AI Application Development Successfully
Success in AI requires different strategies than traditional software projects. These practical guidelines increase your odds dramatically.
Start small with focused use cases. Don't attempt to transform your entire business with AI simultaneously. Pick one painful problem affecting one department. Build a solution. Learn from real usage. Then expand. Small wins build organizational confidence and teach valuable lessons cheaply. Grand visions often collapse under their own complexity.
Focus relentlessly on data before models. The sexiest algorithms fail with poor data. Boring data work determines success. Invest in data infrastructure early. Clean your data obsessively. Label training examples carefully. Validate data quality continuously. Organizations that treat data as a strategic asset succeed with AI. Those that treat it as a technical detail struggle endlessly.
Measure outcomes, not outputs. An AI model with 95% accuracy means nothing if it doesn't improve business metrics. Define success in business terms: revenue increase, cost reduction, customer satisfaction improvement, or time savings. Track these metrics rigorously. Celebrate real business impact, not technical achievements.
Choose partners with proven AI delivery experience. Many software companies claim AI expertise after taking online courses. Actual AI software development companies show portfolios of production systems serving real users. They discuss data challenges openly. They warn about realistic timelines. They know where projects typically fail. Ask potential partners about past failures and what they learned—the honest ones share valuable insights.
Final Thoughts
AI application development stopped being experimental. Companies across industries now depend on AI applications for competitive advantage. The technology works. The tools exist. The question isn't whether to build AI applications but how to build them successfully.
Success depends on clarity about goals, serious commitment to data quality, and realistic execution expectations. Too many organizations rush into AI chasing hype without understanding what success requires. They waste money and lose confidence in valuable technology.
Start with problems where AI offers clear advantages over traditional solutions. Ensure you have data to support model training. Partner with teams who have built similar systems before. Plan for iteration because your first version will teach important lessons. Treat AI as a capability you build over time, not a project you complete and forget.
The planning phase matters more than the algorithms you choose. A well-defined problem with clean data succeeds with basic models. A vague problem with messy data fails regardless of algorithmic sophistication. Do the unglamorous foundational work. The AI will follow.
 Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
What AI applications can you build?
S3Corp builds custom AI applications across major categories: generative AI tools for content and analysis, predictive systems for forecasting and risk assessment, recommendation engines for personalization, conversational AI for customer service, and computer vision for image and video analysis. We focus on applications that solve specific business problems rather than general-purpose AI platforms.
How long does AI application development take?
A minimum viable AI application typically requires 3-6 months from project start to initial deployment. This includes requirements gathering, data preparation, model development, integration, and testing. Full production systems with multiple use cases and comprehensive integration take 6-12 months. Timeline depends heavily on data readiness—projects with clean, labeled data move faster.
How much does AI application development cost?
AI app development cost ranges from $50,000-$150,000 for focused MVPs to $300,000+ for enterprise-scale solutions. Major cost drivers include data preparation work, model complexity, integration depth, and infrastructure requirements. We provide detailed estimates after understanding your specific use case, existing data situation, and integration needs.
What industries do you serve?
S3Corp provides enterprise AI solutions across healthcare, finance, e-commerce, manufacturing, logistics, and education. Our AI consulting and development experience spans predictive maintenance for factories, fraud detection for financial services, recommendation engines for retail, and computer vision for quality control. We focus on industries where we have proven domain expertise.
How do you reduce AI risks like bias and errors?
Our secure AI development process includes bias testing throughout model development, extensive validation with diverse test cases, explainability tools for understanding model decisions, monitoring systems for production behavior, and fallback mechanisms when AI confidence is low. We also help establish governance frameworks for responsible AI deployment.
Why choose S3Corp for AI application development?
S3Corp combines deep technical expertise in AI model development and ML model deployment with practical experience delivering production systems for global enterprises. Our end-to-end AI development process covers strategy, data engineering, model building, integration, and ongoing support. We're transparent about realistic timelines, costs, and challenges because successful AI projects require honest partnerships.
What's the difference between offshore outsourcing and staff augmentation for AI projects?
Offshore outsourcing means S3Corp manages the entire AI project, delivering a complete solution. Staff augmentation provides AI specialists who join your team temporarily, working under your management. Outsourcing works well for defined projects with clear requirements. Staff augmentation suits organizations building internal AI capabilities while accessing specialized skills. We offer both models based on your needs and organizational maturity with AI.



_1746790910898.webp&w=384&q=75)
_1746790956049.webp&w=384&q=75)
_1746790970871.webp&w=384&q=75)
